Influence of the position of keywords on the title
This experiment has the goal of analysing the effect on the ranking of the location of a keyword on the title of a webpage.
Approach
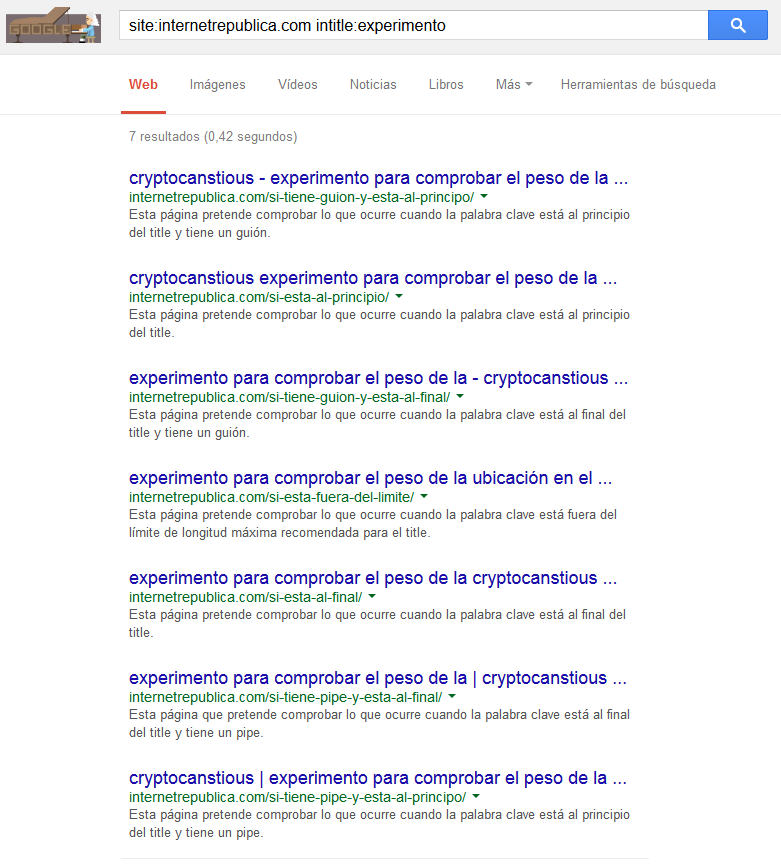
To do the experiment we chose a keyword that we have made up and we have created 7 web pages. In each of them the keyword is in a different position of the title and with different formats:
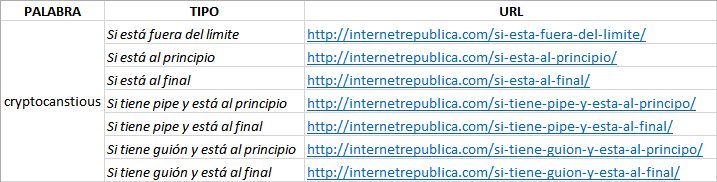
According to the title model that corresponds to each webpage, the result would be:
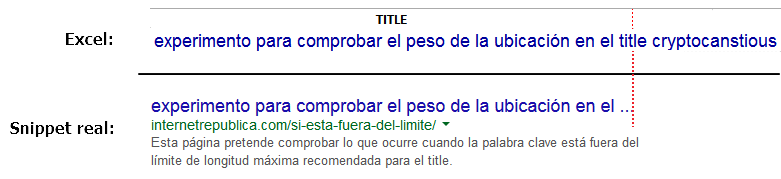
 This Excel spreadsheet shows the column “title” with a special format that emulates the real aspect of the title of a result in a Google SERP. To make this effect we have replicated the font size and typography and we have applied to each column the maximum width recommended by Google for the titles (specified in pixels). Therefore, all what is outside the limit of the column (the red dotted line) would be cut in Google’s result page because it exceeds the recommended length. For example:
This Excel spreadsheet shows the column “title” with a special format that emulates the real aspect of the title of a result in a Google SERP. To make this effect we have replicated the font size and typography and we have applied to each column the maximum width recommended by Google for the titles (specified in pixels). Therefore, all what is outside the limit of the column (the red dotted line) would be cut in Google’s result page because it exceeds the recommended length. For example:
BONUS! Here we leave a link to download the titles simulator. It is a dead simple Excel but it is useful for writing articles and see at a glance how would they look like and if they are going to exceed the recommended length or not: Download
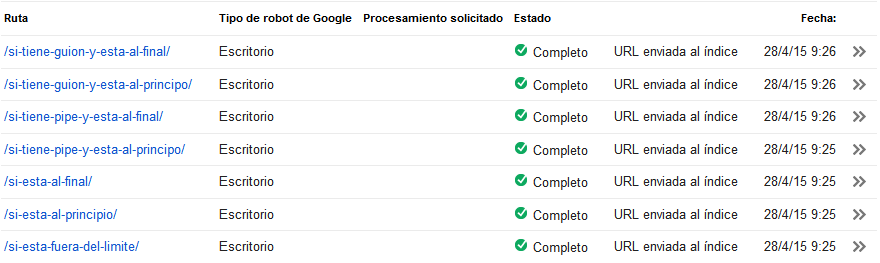
For greater neutrality in the conditions of this experiment, all the pages were published in a lapse of seconds (the content was written each on one tab, publishing all them at once). In the subsequent minutes all the pages were sent to indexation via WMT in a lapse of 1 minute:
Result
Search A. With keyword
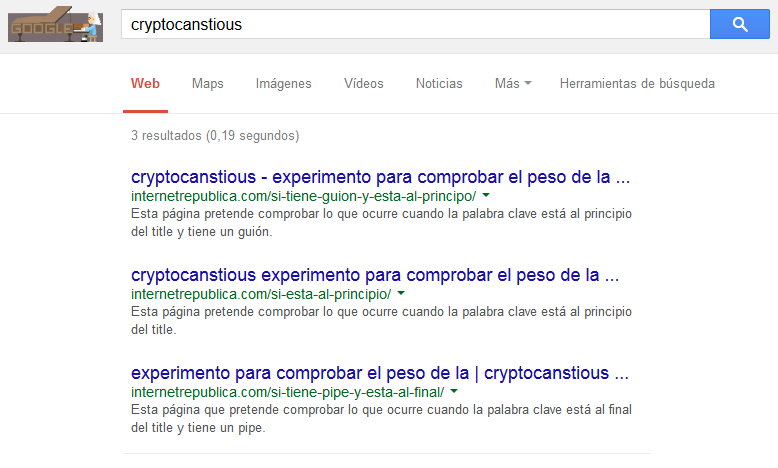 For the normal search there are only three pages:
For the normal search there are only three pages:
- With hyphen, located at the beginning.
- At the beginning.
- With pipe, located at the end.
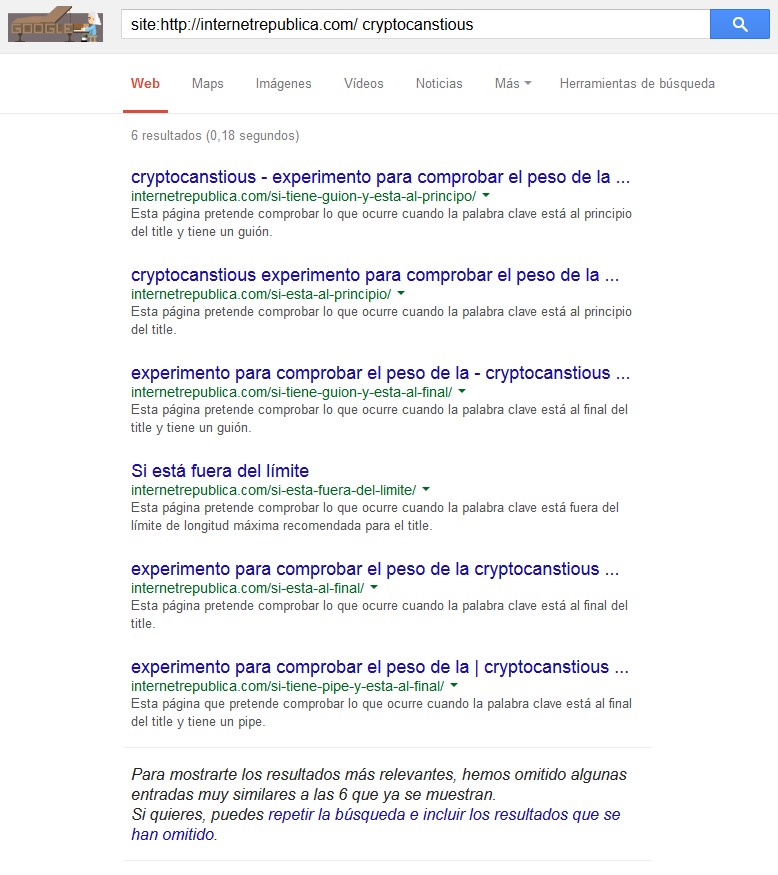
Search B. Using site: + {keyword}
- With hyphen, located at the beginning.
- At the beginning.
- With hyphen, located at the end.
- Outside the limit.
- At the end.
- With pipe, located at the end.
In this case Google is filtering one of the pages (“With hyphen, located at the beginning”) as duplicate content.
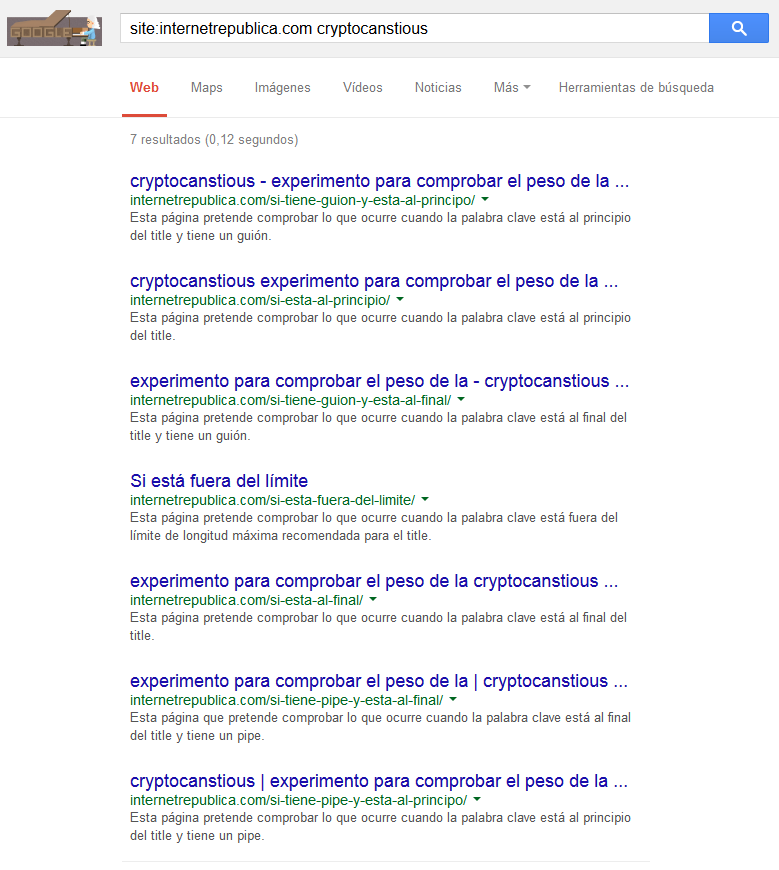
Search C. Using site: + {keyword} – filter duplicate content
We search again deleting the filter to check that the arrangement is the same.
- With hyphen, located at the beginning.
- At the beginning.
- With hyphen, located at the end.
- Outside the limit.
- At the end.
- With pipe, located at the end.
- With pipe, located at the beginning.
Search D. Using site: + {footprint} – filter duplicate content
We search again, and instead of using the keyword we use a footprint (a word repeated in all the pages and which is useful to delimit it in a search). In this case we will use the word “experimento” as a footprint; it appears in the titles of all the pages of this experiment. Doing this we can check how Google responds to the location of the keyword in the title when this keyword is not included in the search.
- With hyphen, located at the beginning.
- At the beginning.
- With hyphen, located at the end.
- Outside the limit.
- At the end.
- With pipe, located at the end.
- With pipe, located at the beginning.
Conclusions
NOTE: The following do not aim to arrive to general conclusions. The intention is to explain what happened in this specific situation under the particular conditions in which the experiment was carried out. We have to take into account that other factors might have had an influence on the result.
– The title model with greatest weight in all the searches was {keyword at the beginning of the title} + hyphen + {text}, followed by {keyword at the beginning of the title} + {text}.
– The titles with pipe were placed at the worst location possible for all the searches.
– Google changes the title of the model that has the word outside the recommended keyword when searches containing the word (searches B and C) are made. It keeps the title the way it was when the same search is made without using the keyword (search D).
– In search A, Google omitted 4 results. This is probably due to the fact that the texts of the webpages and the titles are the same, and the only difference is the location of the keyword (we did it like this to be as neutral as possible). It would be interesting to repeat the experiment modifying the texts so that they are not alike. Then we can compare the differences between the results.
Artículos relacionados
Internet República
Latest posts by Internet República (see all)
- New Instagram update: reel achievements - 19 October, 2023
- Elon Musk has bought Twitter. What does this mean? - 27 April, 2022
- NFTs ARE ARRIVING ON SOCIAL MEDIA - 21 February, 2022