Steps to configure a sitemap file
Before explaining how and why we should configure the sitemap file in our page, we will provide a definition:
What is a sitemap?
It is an XML file that we have to include in our webpage to outlay each of the internal URLs that build up our website and which we want search engines to index.
Why should we include it?
The main functionality of the sitemap file is to make indexation easier for search engines. This file works as an index of the webpages that make up our web, so search engines will be quicker to identify each of the webpages we want to have on the search results.
Steps for a proper configuration of the sitemap file
1. Generate the file sitemap.xml:
To generate the sitemap file we have different options: using plugins, automatic generators or by hand.
In case our webpage has been created on WordPress or similar, there are different plugins that generate the file automatically by crawling the webpages that make up the web. For example: https://wordpress.org/plugins/google-sitemap-generator/
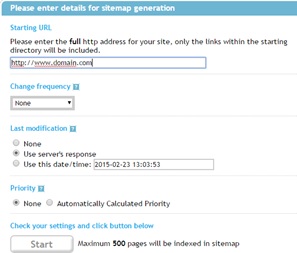
There are also free pages that generate the file automatically including the URL of the webpage you want to crawl. One of the most used ones is www.xml-sitemaps.com
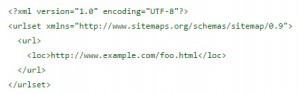
To create the sitemap file manually we have to follow this structure:
There are some compulsory tags we have to include and others that are optional:
Compulsory tags:
- <urlset> (Info about all the URLs included in the file)
- <url> (Specific info about each URL)
- <loc> (Tag where the URL is specified)
Optional tags:
- <lastmod> (Includes the date when the URL was last updated)
- <changefreq> (Indicates the frequency of changes that the page may have)
- <priority> (It sets the priority of a URL over another)
2. Indexing the file sitemap.xml:
After we have generated the file we have to index it. How? First we have to upload the generated file to our webpage. It is recommended that we include the root of the web (www.domain.com/sitemap.xml)
The second step is to tell searches where it is located. We have to upload the file using Webmaster Tools or webmaster tools for searches like Bing or Yahoo.
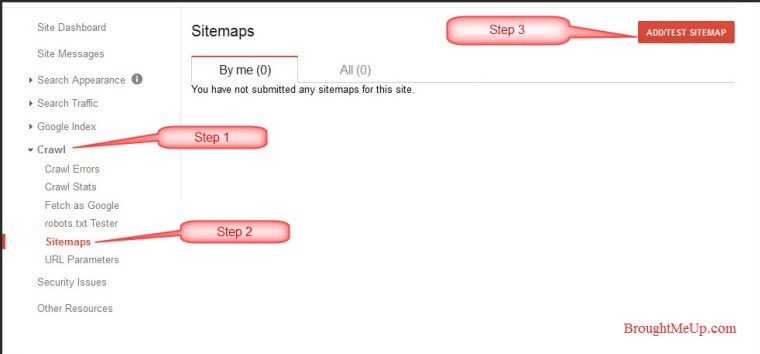
Once in WMT we have to go to https://www.google.com/webmasters/tools/home
Under “Crawl/Sitemaps” we have to add our sitemap including the URL of our webpage and send it.
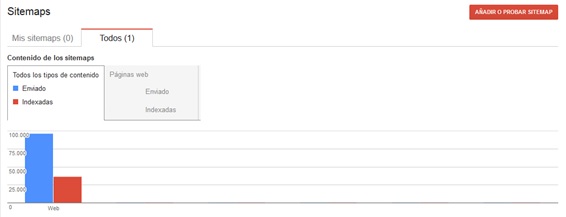
Once sent, the tool will tell us the number of pages sent, and when Google spiders crawl the page we will see the amount of pages indexed out of the total included in the sitemap.
This is very useful to detect indexing errors of our webpage, since from Webmaster Tools we can check out which pages have not indexed and why under “Crawling errors.”
Types of sitemap:
In addition to indicate the URL structure of our webpage, we can use the sitemap file to indicate the existence of other kinds of content like pictures, videos, news or mobile specifications.
The extensions for this kind of content on the sitemap are:
Sitemap Images: xmlns:image=http://www.google.com/schemas/sitemap-image/1.1
Sitemap Video: xmlns:video=http://www.google.com/schemas/sitemap-video/1.1
Sitemap Mobile: xmlns:mobile=http://www.google.com/schemas/sitemap-mobile/1.0
Sitemap News: xmlns:news=http://www.google.com/schemas/sitemap-news/0.9
Other recommendations:
- Include the sitemap also in the file robots.txt.
Another way to index more quickly our webpages is including the sitemap route within the robots.txt file so that we tell the search engines where it is located.
To include it, we just have to indicate the route of the sitemap-preferably under the last line of the robots file-as follows:
Sitemap: www.domain.com/sitemap.xml
- Divide up the sitemap file if your webpage generates a high amount of URLs.
Some pages have a very high amount of URLs. To improve and control more efficiently the indexation of these we can generate different sitemap.xml files structured by section, category, etc.
The maximum amount of URLs that a sitemap file can have is 50,000, provided that the total file size is not over 50MB. However, it is not recommended to get close to these limits, creating always smaller sitemaps.
Moreover, remember that through Webmaster Tools you can control the indexing errors of each URL, so that in case of having a very big website this will help us locate easily the indexing errors.
- Use the sitemap file to include alternative tags.
We can also use the sitemap file to point towards other relevant tags for the content of our page, like for example the hreflang tag to indicate the languages in which our page is shown.
- Update the sitemap periodically.
The sitemap file has to be updated every time that new URLs are generated and indexed. When it is updated we have to send it again using the aforementioned tools for a proper indexation.
Interesting links:
- https://support.google.com/webmasters/answer/183668?hl=en&ref_topic=6080646&rd=1
- http://www.sitemaps.org/
Image via Balakov.
Artículos relacionados
Internet República
Latest posts by Internet República (see all)
- New Instagram update: reel achievements - 19 October, 2023
- Elon Musk has bought Twitter. What does this mean? - 27 April, 2022
- NFTs ARE ARRIVING ON SOCIAL MEDIA - 21 February, 2022